Technology:
Various
Dimensional accuracy:
Typically in the range of 100 to 300 microns (0.1mm to 0.3mm)
Build Volume Space:
Various
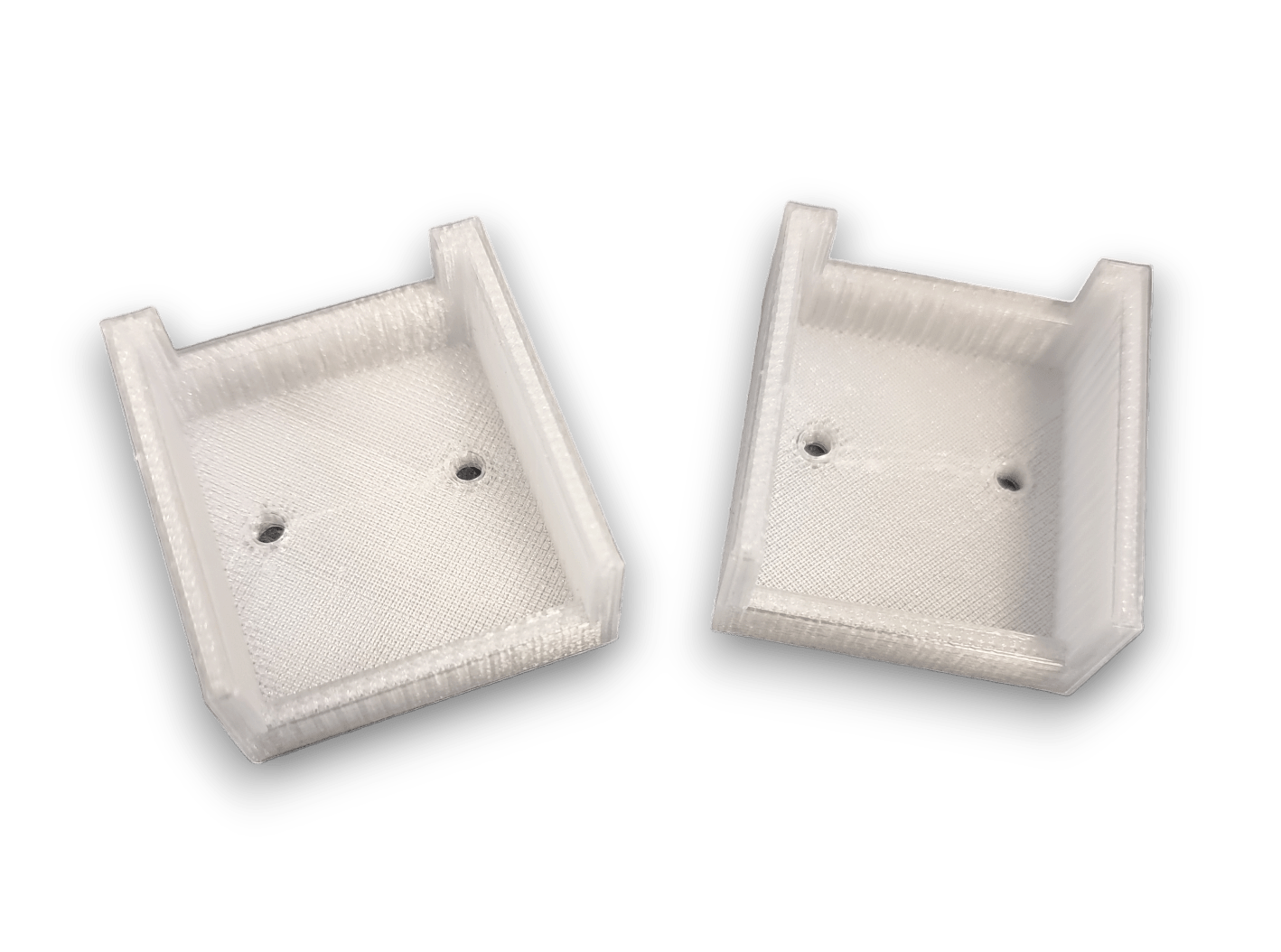

Filaments are the building blocks of Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), a popular 3D printing technology. These thermoplastic filaments are heated and extruded through a nozzle to create layers, shaping a 3D printed object. FDM printing offers a diverse range of filaments, each with distinct properties tailored for various applications.